LPCVD (Low Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition) is widely used in chip manufacturing to create various thin films with different purposes. It can be employed for depositing silicon dioxide and silicon nitride films, as well as for producing doped films to modify the conductivity of silicon.



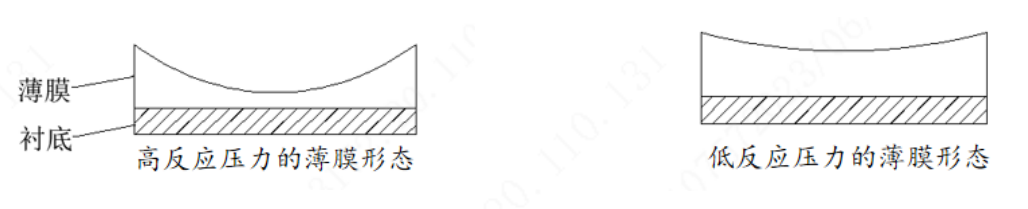
Why is low pressure used? Lower pressure leads to better uniformity within the wafer. Under high-pressure conditions, the diffusion of reaction gases in the middle region of the wafer is less effective. In contrast, under low-pressure conditions, the reactant gases can freely move and diffuse more efficiently.
Back

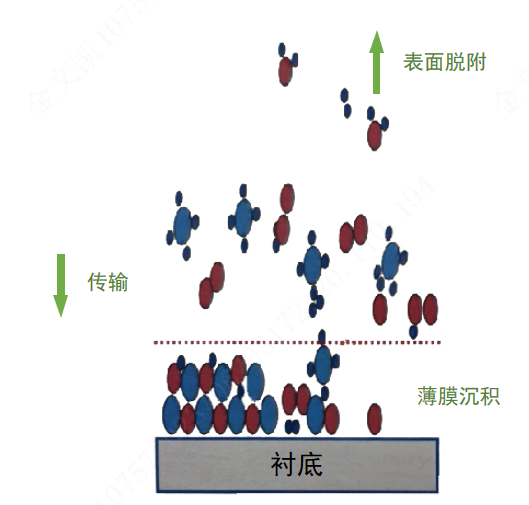
Principles of LPCVD deposition:
1.Introduction of reaction gases: The reaction gases are introduced into the deposition tube, which is maintained at a low pressure, typically around 0.25-1Torr.
2.Transport of reactants to the surface: Under the low-pressure condition, the reactants can freely move on the surface of the wafer.
3.Adhesion of reactants to the substrate surface.
4.Heat-induced chemical reactions on the wafer surface, leading to the formation of reaction products.
5.Removal of excess gases from the surface.
6.Accumulation of reaction products on the surface to form a film.

LPCVD systems can be classified into vertical and horizontal configurations. Vertical and horizontal LPCVD systems are two common types of LPCVD systems named after the orientation of the furnace or the placement of the substrate. The main difference between these two systems lies in the substrate placement and the flow of gases. In the late 20th century, many LPCVD processes were performed in horizontal hot-wall reactors, but nowadays vertical furnaces are predominantly used.

臥式LPCVD機臺

立式LPCVD機臺
Laplace LPCVD Furnace Series
Why is low pressure used? Lower pressure leads to better uniformity within the wafer. Under high-pressure conditions, the diffusion of reaction gases in the middle region of the wafer is less effective. In contrast, under low-pressure conditions, the reactant gases can freely move and diffuse more efficiently.